Multiple Opening Analysis
Did you know that if you have a bridge opening and one or more culverts at a single river crossing a Multiple Opening Analysis is required?
Though it’s not very common, it is possible to get negative flows over inline structures for unsteady flow simulations. It’s much more likely you’ll see negative flows over a lateral structure though. Negative flows are simply discharges in your model going the opposite direction than what you have defined as the downstream direction (or primary flow direction). This can occur in tidal areas, backwater, or complex looped networks. For lateral structures, you may have water spill out of your river over a lateral structure and into a storage area. Once the flood wave passes, the head level in the storage area is higher than the river and water flows back into the river (negative flow). It’s called negative flow because RAS will show it in tables and plots as a negative number.
Recently, an HEC-RAS output table issue was brought to my attention, directly related to negative flows over weirs.
“I was looking through the HEC-RAS file for the XYZ model for the 72-hr PMF and came across the following. Do you know what -1.#INF means?”
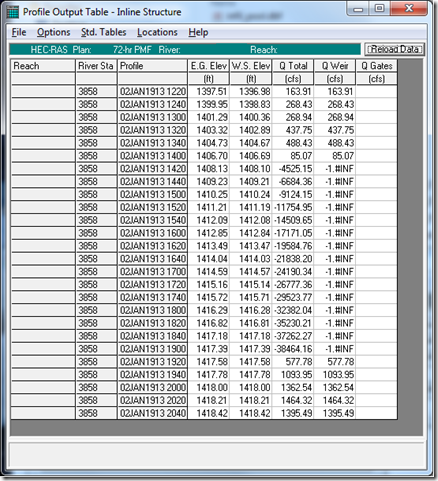
In this example, the water surface elevation downstream of the inline structure exceeds the water surface elevation upstream of the inline structure between the time of 1420 hrs and 1900 hrs on 02 January, 1913. During this time range, we have a negative head differential and thus a negative flow over the inline structure (from downstream to upstream). During a simulation, when an inline structure is overtopped by water, RAS uses the same equation (the weir equation with adjustments for submergence) regardless of the direction of flow over the inline structure. The -1.#INF is the double precision floating point default return in the Visual Basic programming language for any unreal number (i.e. you may remember imaginary numbers, “i” from high school math class). Well RAS is trying to take a negative number (in this case the head differential) to a non–integer power, (1.5 for the weir equation, Q = CLH^1.5). There is no real solution for this. The good news is, this is only happening in the table, as RAS recomputes the Q Weir to populate the table using the steady flow engine. Presumably, that is why RAS cannot deal with negative head differentials, since there is no negative flow in steady flow modeling. During the unsteady flow computations, RAS correctly removes the negative sign to do the computations and then replaces it to show flow in the “negative” direction. That’s why the computations work and why the Q Total is negative (which is presumably what Q Weir should be in this example). So, in short, the unsteady flow computations are fine-the solution is correct. The problem comes when reporting results to the Inline Structure Table. Hopefully this will be fixed for the next version of HEC-RAS. Until then, you can use the stage and flow output hydrographs to verify the total and weir Q’s.
Comments
abdelbaset midaoui
on January 28, 2015this is happened with me also at junction between two rivers. notice that there is an other problem apart negative flow : the exaggerated flow values !!
any explanation for that?
thanks a lot.
abdelbaset midaoui
on January 28, 2015This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
Chris Goodell
on February 1, 2015Check your junction lengths and make sure they are correct. Also review these posts-they may help explain the problem.
http://hecrasmodel.blogspot.com/2008/12/unsteady-flow-and-junctions.html
http://hecrasmodel.blogspot.com/2011/05/modeling-junctions-for-unsteady-flow.html
http://hecrasmodel.blogspot.com/2009/02/severe-energy-jump-at-junctions-for.html
Unknown
on January 26, 2017A lateral structure I am using to model overflow from the main channel into a side channel is showing a negative discharge for several profiles. What's interesting is that the negative discharge values are far in excess of the discharge in the side channel. The side channel only has 0.1 cfs running through it, but after optimizing the lateral structure, the profile output table shows -425 cfs entering the main channel from the side channel. Do you know why this would be? The profiles showing the negative discharges do not exceed the sides of the cross section on the main channel; the profiles that do fail to converge when optimized.
Chris Goodell
on January 27, 2017Yes, that doesn't make sense. If optimization fails to converge, you can get weird results like this. Otherwise I'm not sure what could cause this.
Sam Plaza
on January 27, 2017What's weird is that the profiles showing the negative discharge do converge when optimized; the profiles which do not converge do not show this excess negative discharge.
Angana Borah
on March 27, 2018I modeling one stretch of a big continuous river, and there are tributaries joining the river at different cross sections along the river, but instead of creating internal boundary conditions I am using single initial condition at upstream. Is it okay to do that because even i am getting negative flows for a few days.
Chris Goodell
on April 5, 2018It’s realy up to you to decide how much of an impact the tribe will have on your river. If negligible impact, go ahead and ignore them.
CJ
on January 7, 2019Any solutions for this issue?
Roy
on June 18, 2020Hello,
I am using HEC-RAS 5.0.3.
I have a problem regarding negative flows in my 2D area. I have drawn a profile line on my 2D grid and this profile line shows negative flows through this profile. But when I watch the flow pattern with the static velocity arrows enabled, these arrows only point into the positive direction. Also the velocity profile over the profile line that I have drawn only shows positive numbers. Can this be solved?
Chris Goodell
on June 18, 2020It’s not advised to look at flows on a profile line drawn in the direction of flow. It doesn’t really make sense. The flows measured on a profile line tell you how much water is passing through the line, not going along it. You should only look at flows on profile lines drawn transverse to flow.
Add Your Comment